Unit Element Fixed Rubber Fenders: The Backbone of Quay Wall Protection
25/12/2025What Are the Applications of Buoyancy Rubber Airbags?
01/01/2026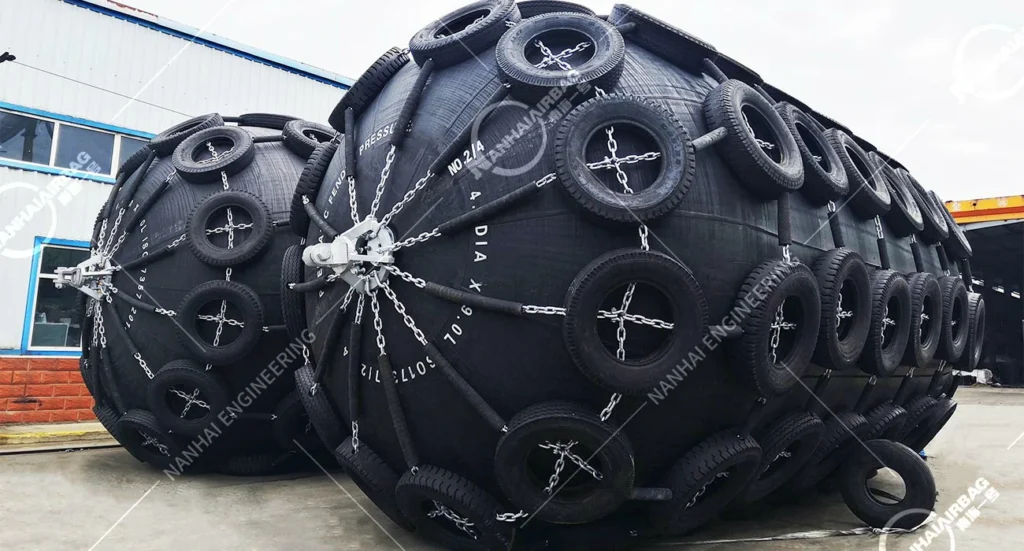
Navigating the world of marine protection can be complex, but selecting the correct fender is non-negotiable for safeguarding both your assets and your operations. Pneumatic fenders, a specialized type of marine fender, offer unique advantages for a variety of berthing scenarios. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to make an informed decision.
Google Selected Summary: Your Guide to Selecting Pneumatic Fenders
Choosing the right pneumatic fender requires a thorough evaluation of your specific berthing conditions. Key factors include the vessel’s size and tonnage, the available berthing space, and the required energy absorption. A correctly selected pneumatic fender provides a low-reaction force and high-energy absorption, making it ideal for protecting large vessels and delicate structures. Unlike solid rubber fenders, these inflatable units offer superior performance for varying water levels and tidal ranges. Investing in a high-quality pneumatic fender means prioritizing marine-grade rubber, robust end fittings, and adherence to international standards like ISO 17357. This ensures longevity and reliability, positioning pneumatic fenders as a premium choice within the broader category of rubber fenders. Their design principle shares similarities with marine airbags, utilizing compressed air for efficient energy dissipation.
The Clear Advantages of Pneumatic Fenders (With Real-World Examples)
Pneumatic fenders are not just another option; they are a superior solution in many scenarios. Their design provides distinct benefits that static or solid rubber fenders cannot match.
- Advantage: Exceptional Energy Absorption with Low Reaction Force. Example:A major LNG terminal in Qatar uses large pneumatic fenders to berth massive Q-Max tankers. The fenders absorb the enormous kinetic energy of these giants, protecting the expensive cryogenic loading arms with minimal stress transferred to the terminal structure.
- Advantage: Unsinkable and Self-Floating. Even if punctured, the fender remains afloat. Example:An offshore supply base in the North Sea relies on pneumatic fenders for transferring supplies to drilling platforms. In rough seas, a punctured fender would sink, but the self-floating nature of pneumatic fenders ensures continuous operation.
- Advantage: Versatility in Draft and Tidal Changes. The free-floating nature allows them to adjust vertically with changing tides. Example:A historic ferry port in Venice, Italy, with significant tidal fluctuations, uses pneumatic fenders to ensure consistent protection for its heritage piers regardless of the tide level.
- Advantage: Ease of Installation and Relocation. They can be quickly deployed and moved as needed. Example:During the construction of a new bridge, engineers used pneumatic fenders as temporary protection for support pillars, easily relocating them as the construction zone shifted. This flexibility is akin to the deployment of marine airbags during ship launching.
Engage: Are You Overpaying for Inadequate Protection?
Your port’s efficiency and safety hinge on a single piece of equipment: the fender. Choosing the wrong one can lead to vessel damage, infrastructure repairs, and costly downtime. So, how do you navigate the technical specifications to find the perfect fit? The answer lies in understanding the critical selection criteria.
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Fender: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Calculate the Required Energy Absorption
This is the most critical step. You must calculate the berthing energy of your largest expected vessel. This involves knowing the vessel’s displacement, velocity at impact, and the berthing angle. Consult with a fender specialist or use online calculators to determine the required Energy Absorption (E) and Reaction Force (R).
2. Select the Appropriate Size and Diameter
Pneumatic fenders come in various diameters and lengths. A larger diameter generally provides higher energy absorption and lower reaction force. Match the fender’s performance curves (provided by manufacturers) to your calculated E and R values.
3. Inspect Material Quality and Construction
A pneumatic fender is a sophisticated rubber fender. Look for:
- Multi-layer construction: A tough outer rubber skin, a reinforced cord layer (like nylon or polyester), and an inner airtight rubber bladder.
- Marine-grade rubber compounds resistant to ozone, UV, and seawater.
- Robust end fittings (e.g., swivels, chains, shackles) made from stainless steel or hot-dip galvanized steel.
4. Verify Safety Standards and Certifications
Ensure the fenders comply with international standards, primarily ISO 17357. This certification guarantees the fender meets minimum performance and safety requirements. Ask the supplier for test certificates and quality control documentation.
5. Consider the Application Environment
- Permanent or Temporary Use? Pneumatic fenders are excellent for both. For permanent installations, consider protective sleeves to prevent mechanical damage.
- Harsh Environments? If operating in very cold climates, ensure the rubber compound is suitable for low temperatures. For tropical zones, focus on UV resistance.
- Comparison to Other Systems: While solid marine fenders are durable, they lack the low-reaction force of pneumatics. Foam-filled fenders are an alternative but are heavier and harder to handle. Like marine airbags, pneumatic fenders are prized for their high performance-to-weight ratio.
Related Questions (FAQs)
- What is a pneumatic fender? A pneumatic fender (also known as a Yokohama fender or floating fender) is an inflatable rubber fender filled with air under pressure. It is used to absorb the kinetic energy of a berthing vessel.
- What is the difference between pneumatic fenders and foam-filled fenders? Pneumatic fenders are filled with air and can be deflated for transport. Foam-filled fenders are filled with polyurethane foam and are always buoyant. Pneumatic fenders generally offer better energy absorption characteristics.
- How long do pneumatic fenders last? With proper care and maintenance, a high-quality pneumatic fender can last 10-15 years. Regular inspections for cuts, abrasions, and leaks are essential.
- How are pneumatic fenders maintained? Maintenance includes regular visual inspections, checking air pressure, cleaning the surface, and ensuring end fittings are secure.
- Can pneumatic fenders be used for small boats? Yes, they are available in a wide range of sizes, from small boat fenders to those capable of protecting supertankers.
- What is the relationship between marine airbags and pneumatic fenders? Both are made from durable rubber and use compressed air for their function. However, marine airbags are primarily used for ship launching and salvage, while pneumatic fenders are designed for vessel protection during berthing.
Final Recommendation
Choosing the right pneumatic fender is an investment in safety and efficiency. By carefully analyzing your operational needs and understanding the product’s capabilities, you can select a marine fender that delivers unparalleled protection for years to come. Always consult with reputable manufacturers to get the right advice and products for your specific application.
Keywords integrated: marine airbags, marine fenders, rubber fenders.
